Understanding Fungal Infections: Causes, Types, and Treatment
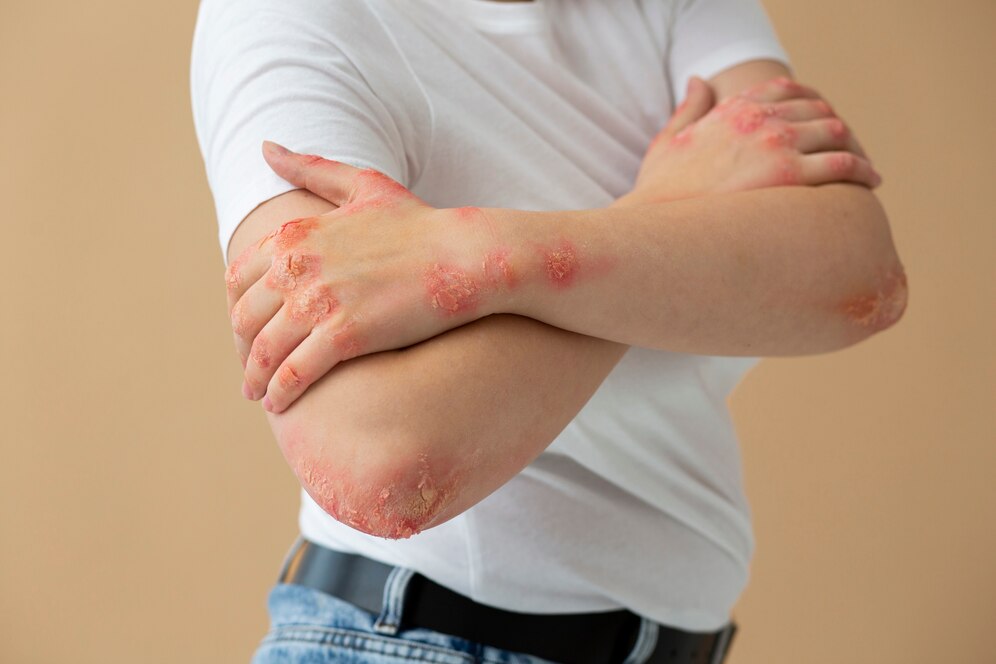
Fungal infections, also known as mycosis, are skin diseases caused by fungi. Fungi are ubiquitous organisms found in water, soil, plants, and even on the human body. These infections thrive in warm, moist environments, making areas such as the feet, groin, and skin folds susceptible to infection. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the causes, types, symptoms, and treatment options for fungal skin infections.
Causes of Fungal Infections:
Fungal infections occur when fungi invade the skin and multiply in warm, moist areas of the body. Common causes include:
- Direct contact with fungi on contaminated surfaces, clothing, or items
-
Sweaty or damp skin that lacks proper airflow
- Weakened immune system
- Certain medical conditions or medications that increase susceptibility to fungal infections
Types of Fungal Infections:
Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis):A common fungal infection that affects the feet, particularly between the toes. Symptoms include white, peeling skin and itching.
Nail Fungus (Onychomycosis):Fungal infection of the nails, typically affecting the toenails. Infected nails may become thick, discolored, and brittle.
Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris):A fungal infection that causes a rash in the groin area, more common in men than women. Symptoms include redness, itching, and a rash that may spread to the thighs.
Scalp Ringworm (Tinea Capitis): This fungal infection primarily affects children and can lead to hair loss. It presents as circular patches of scaly, reddish skin on the scalp.
Ringworm (Tinea Corporis): Despite its name, ringworm is a fungal infection characterized by circular, scaly patches on the skin. It can affect any part of the body and is highly contagious.
Symptoms of Fungal Infections:
Symptoms of fungal infections may vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Redness, itching, and irritation
-
Peeling, cracking, or scaling of the skin
- Discoloration or thickening of the nails
- Rash or circular patches of inflamed skin
- Hair loss (in scalp infections)
Treatment Options:
Treatment for fungal infections typically involves a combination of oral and topical antifungal medications to eradicate the fungus and alleviate symptoms. Other treatment measures may include:
- Keeping the affected area clean, dry, and well-ventilated
-
Avoiding tight-fitting clothing and shoes
- Using antifungal powders or sprays to prevent recurrence
- Practicing good hygiene, including regular handwashing and avoiding sharing personal items with others
Conclusion:
Fungal infections can cause discomfort and inconvenience, but prompt identification and treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. If you suspect you have a fungal skin infection or experience persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.