Understanding Allergies and Hives: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
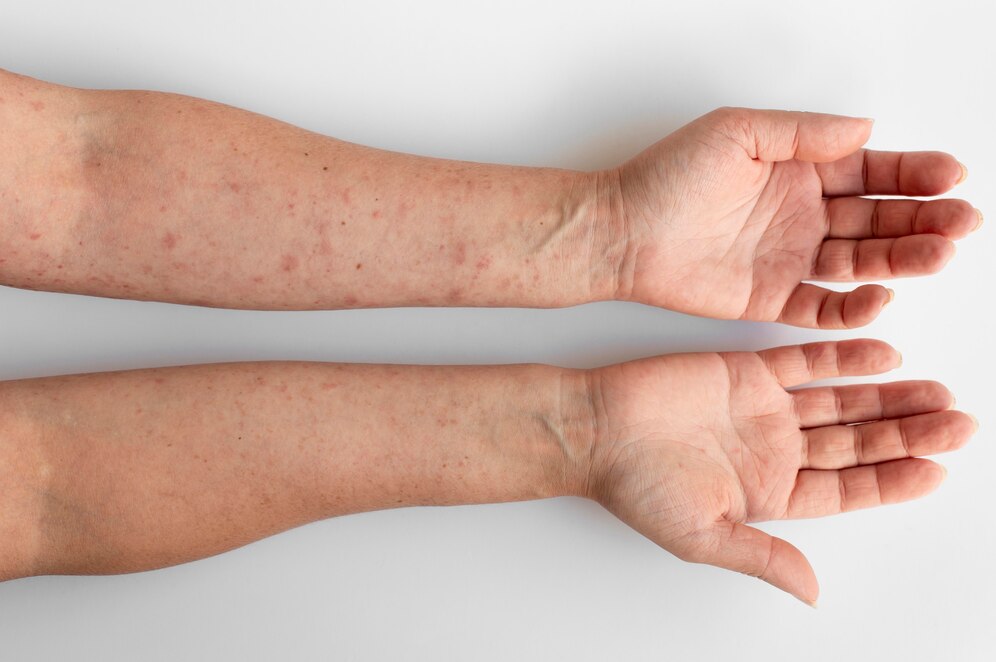
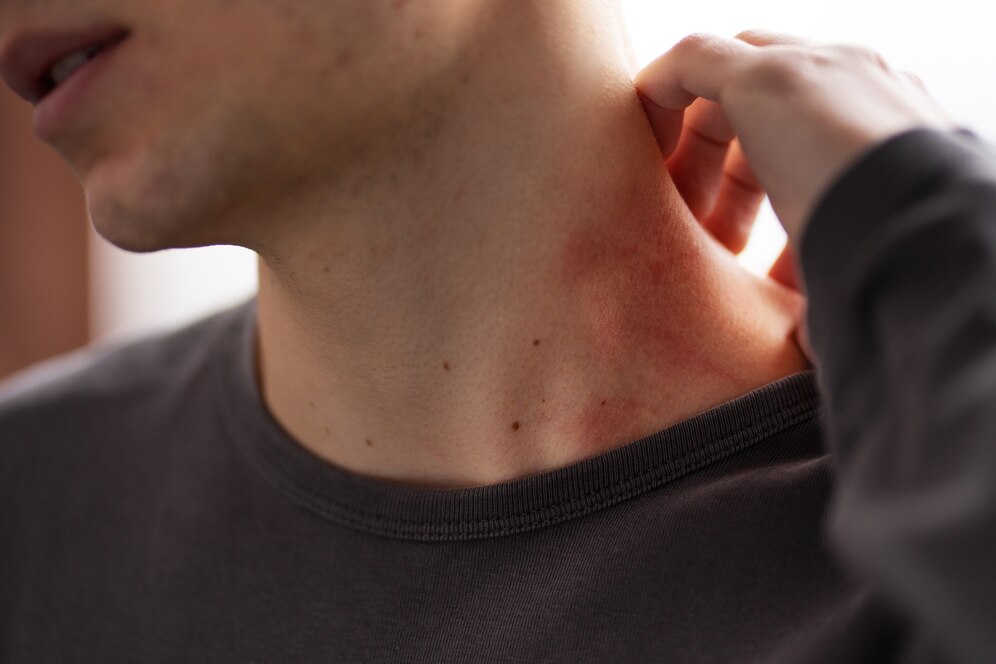
Hives, also known as urticaria, are red, raised, and sometimes itchy bumps that appear on the skin. They are a common manifestation of an allergic reaction triggered by various allergens. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for managing allergies and hives effectively.
Causes of Hives:
Hives occur when the body's immune system releases chemicals, such as histamine, in response to an allergen or trigger. Common causes of hives include:
Drugs or Food: Certain medications or food allergens can provoke an allergic reaction, leading to the development of hives.
Infections: Viral or bacterial infections, such as colds or sinus infections, can sometimes trigger hives.
Infestations: Parasitic infestations, such as scabies or bed bug bites, may cause hives in some individuals.
Contactants: Exposure to allergens in the environment, such as pollen, animal dander, or latex, can lead to hives upon contact.
Inhalants: Breathing in allergens like pollen, dust mites, or mold spores can trigger an allergic response, resulting in hives.
Stress: Emotional stress or anxiety can sometimes exacerbate hives or act as a triggering factor.
Symptoms of Hives:
Hives typically present as red, raised welts or bumps on the skin that may vary in size and shape. Key symptoms include:
- Itching or burning sensation
- Swelling of the affected area
- Blanched appearance when pressed (skin turns white and then red when released)
- Rapid onset and resolution
- Hives may appear and disappear within hours, only to reappear elsewhere on the body.
Treatment Options for Hives:
Treatment for hives aims to alleviate symptoms and identify and address the underlying cause of the allergic reaction. Common treatment options include:
Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines, such as loratadine or cetirizine, can help relieve itching and reduce the severity of hives.
Topical Treatments:Calamine lotion or hydrocortisone cream may be applied to the affected areas to soothe itching and inflammation.
Avoidance of Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as specific foods, medications, or environmental allergens, can help prevent recurrent episodes of hives.
Emergency Treatment:In severe cases of hives accompanied by difficulty breathing or swelling of the throat, emergency medical attention is necessary. Epinephrine injections may be administered to treat anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction.
Conclusion:
Hives are a common allergic reaction characterized by red, raised welts on the skin. While they can be bothersome, timely identification of triggers and appropriate treatment measures can help manage symptoms effectively. If you experience recurrent or severe hives, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.